Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Electronic Engineering, Heilongjiang University, Harbin 150080, China
2 Physics Group, Chaoyang Medical School, Chaoyang 122000, China
3 College of Physics, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
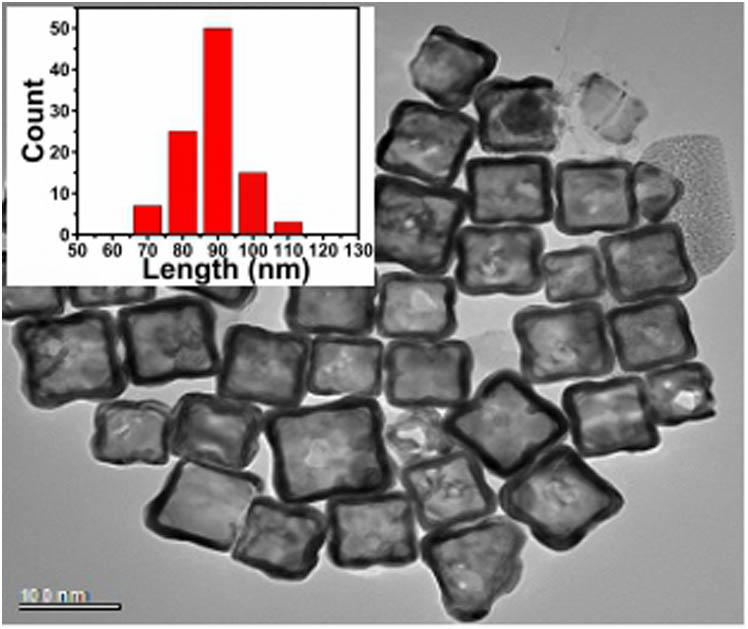
The dipole resonances of gold nanocages were investigated theoretically using finite difference time domain method. The results show that field enhancement is obtained at the walls of the gold nanocages. It is believed that the effect can cause a strong optical nonlinear property. To test the hypothesis, nonlinear absorption was investigated using a broadband 5 ns Z scan. It was found that at low intensities the sample shows saturable absorption (SA), while at higher intensities a switch from SA to reverse SA occurs. Moreover, the nonlinear absorption of the sample is sensitively wavelength-dependent, and, in the resonant region, saturation intensity is the largest.
saturable absorption reverse saturable absorption gold nanocages FDTD Z-scan Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(1): 011901
Author Affiliations
Abstract
College of Electronic Engineering, Heilongjiang University, Harbin 150080, China
Extraordinary optical transmission (EOT) in subwavelength metal structures has been studied widely. Herein, we propose a strategy for tuning the EOT of the bullseye structure. Specifically, the bullseye structure was immersed in a nonlinear medium, and a controlling light was employed to change the refractive index of the medium. At different intensities and distributions of controlling light, the transmission property of signal light in the bullseye structure was simulated. The results show that a variable transmission spectrum in the bullseye structure can be realized. Moreover, the position of the central transmission peak shifts linearly with the increasing intensity of controlling light.
230.3990 Micro-optical devices 130.6010 Sensors Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(12): 122302
1 黑龙江大学 电子工程学院, 黑龙江 哈尔滨 150080
2 黑龙江工程学院 电气与信息工程学院, 黑龙江 哈尔滨 150050
周期性亚波长孔阵列的异常透射性质在亚波长光电器件设计中具有重要意义。两层或更多膜层上周期孔阵列结构, 由于层之间电磁场的相互作用可以导致新的光学性质。利用时域有限差分方法理论研究了带有矩形孔阵列的Au-介质-Au多层膜的透射特性。结果表明: 该结构在近红外波段的透射谱存在多个透射峰, 并且透射峰的数量、位置和强度可以通过改变结构的几何参数和介质膜的材料进行调控。详细分析了介质膜的厚度和折射率、孔阵列的周期、矩形孔的边长等因素对多层膜矩形孔阵列透射谱的影响, 为利用多个表面等离子共振设计多波长控制器件提供了一定的参考。
多层膜 矩形孔阵列 异常透射 表面等离极化激元 时域有限差分法 multilayer films rectangular hole arrays extraordinary optical transmission surface plasmon polaritions finite difference time domain method 红外与激光工程
2019, 48(7): 0721001
黑龙江大学 电子工程学院, 黑龙江 哈尔滨 150080
金属纳米粒子的尺寸和形状对其物理和化学性质有很大影响, 通常利用昂贵的透射电子显微镜和扫描电子显微镜进行其尺寸测量。为了节约测量成本, 利用时域有限差分法研究了金纳米棒的尺寸与吸收峰的对应关系得到间接的测量方法。即当金纳米棒的纵横比增大时, 横向等离子峰几乎没有变化, 纵向等离子峰出现明显的红移, 且红移速度随着金纳米棒半径的增大而增大。实际制备了两种不同尺寸的金纳米棒样品, 通过理论模拟确定的金纳米棒的尺寸与利用透射电子显微镜测量的金纳米棒的尺寸符合的很好。
光谱学 表面等离子体共振 时域有限差分法 金纳米棒 吸收光谱 尺寸 spectroscopy surface plasmon resonance (SPR) finite difference time domain method (FDTD) gold nanorods absorption specturm size
1 黑龙江大学电子工程学院,黑龙江 哈尔滨 150080
2 辽宁省朝阳师范高等专科学校信息工程系,辽宁 朝阳 122000
牛眼结构是一种典型的纳米光学结构。本文设计了一种带有同轴纳米柱的牛眼结构,利用时域有限差分法(FDTD)研究了该结构的增强透射效应。研究发现,柱的半径和高度对透射特性具有显著的影响,恰当选择柱的半径和高度会得到最大的透射强度。另外,牛眼结构对环境折射率有较高的灵敏度。理论分析表明,该种结构的透射增强效应是由局域表面等离激元与表面极化等离激元相互作用产生。这为纳米光学元件的研发与应用提供一个新的思路。
表面等离激元 光异常透射 牛眼结构 时域有限差分法 surface plasmon EOT bullseye structure finite difference time domain method
黑龙江大学 电子工程学院, 黑龙江 哈尔滨 150080
物体的热膨胀性质反映了材料本身的属性, 通常将固体受热后在一维方向上长度的变化称为线膨胀。测量材料的线膨胀系数, 不仅对新材料的研制具有重要意义, 而且也是选用材料的重要指标之一。将激光外差技术与多普勒效应深度融合, 提出一种多光束激光外差测量金属线膨胀系数的新方法, 即利用多普勒振镜把待测参数信息调制到多光束激光外差信号的频率差中, 信号解调后可以同时获取多个待测参数信息, 对多个待测参数加权平均, 从而可以精确得到待测样品长度随温度的变化量, 最终提高待测样品线膨胀系数的测量精度。基于该方法, 对不同温度情况下金属棒线膨胀系数进行了仿真研究, 结果表明该方法测量金属棒线膨胀系数的相对误差为0.1%。与传统测量方法相比, 测量精度提高了一个数量级。
线膨胀系数 多光束激光外差 多普勒效应 linear expansion coefficient multi-beam laser heterodyne Doppler effect 红外与激光工程
2018, 47(7): 0706005
黑龙江大学 电子工程学院, 黑龙江 哈尔滨 150080
利用飞秒脉冲通过Z扫描技术和泵浦-探测技术研究了CdS0.2Se0.8纳米晶掺杂的硼酸盐玻璃滤波片RG665的非线性吸收特性。研究结果表明在800 nm波长 130 fs脉冲激光作用下, RG665滤波片表现较强的非线性吸收特性。通过理论分析拟合实验结果证明RG665滤波片在800 nm下的非线性吸收包含双光子吸收及双光子吸收诱导的激发态吸收两部分, 得到双光子吸收系数为0.05 cm/GW, 激发态吸收截面为σe=3×10-23 m2, 以及导带中低能态电子和导带底电子的寿命分别为13 ps和210 ps。研究结果表明CdS0.2Se0.8纳米晶体掺杂的玻璃是一种很好的非线性光学材料。
Z扫描 非线性吸收 双光子吸收 激发态吸收 Z-scan nonlinear absorption two-photon absorption excited state absorption 红外与激光工程
2017, 46(3): 0321004

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Postdoctoral Mobile Research Station of the School of Electronic Engineering, Heilongjiang University, Harbin 150080, China
2 School of Applied Sciences, Harbin University of Science and Technology, Harbin 150080, China
3 Key Laboratory of Electronics Engineering, College of Heilongjiang Province, Heilongjiang University, Harbin 150080, China
We experimentally investigate the effects of the surface roughness of gold thin films on the properties of surface plasmon resonance. By annealing at different temperatures, film samples with different surface morphologies are obtained. Specifically, due to the diffusion of the gold atoms towards the films’ surface, the surface root-mean-square roughness decreases with the increasing annealing temperature. Then, we measure the surface plasmon resonance of the samples. The results show that the resonance angle of the surface plasmon resonance is sensitive to the root-mean-square roughness, and it gradually decreases by reducing the surface root-mean-square roughness.
240.6680 Surface plasmons 310.6860 Thin films, optical properties Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(4): 042401
黑龙江大学电子工程学院,黑龙江 哈尔滨 150080
应用Z-扫描技术对比研究了萘酞菁铅和萘酞菁钯化合物在波长为532 nm纳秒激光脉冲作用下的三阶非线光学特性。实验结果表明,两种萘酞菁化合物均显现出较强的非线性吸收特性(反饱和吸收)和非线性折射特性(自聚焦)。理论拟合得出萘酞菁铅和萘酞菁钯的非线性吸收系数β分别为6.54×10-10 m/W和3.90×10-10 m/W;非线性折射系数率n2分别为1.68×10-10 esu和8.04×10-11 esu;二阶分子超极化率系数γ分别为3.44×10-28 esu和2.57×10-28 esu,CS2二阶分子超极化率系数为4.32×10-33 esu;两种萘酞菁化合物的二阶分子超极化率强于CS2近5个数量级。实验结果表明,萘酞菁铅化合物具有较强的非线性吸收和非线性折射特性,且大于萘酞菁钯化合物的光学非线性特性是由于萘酞菁铅化合物的重原子效应提高了其光学非线性特性。
三阶光学非线性 萘酞菁 重原子效应 third-order optical nonlinearity naphthalocyanine heavy atom effect
黑龙江大学电子工程学院, 黑龙江 哈尔滨 150080
利用飞秒激光直写加工平台,对飞秒激光脉冲与半导体硅材料相互作用进行了研究。在不同的激光功率和脉冲数作用下,通过定点辐照和扫描方式在硅表面进行微结构诱导。用扫描电子显微镜对表面诱导结构进行表征,实验发现激光功率和脉冲数影响诱导微结构的形貌和周期,并发现诱导得到的周期性条纹结构的取向与诱导激光的偏振方向有关,通过调整激光的偏振方向可以有效地控制结构的取向。通过扫描的方式,可以在硅材料表面制备排列规则的周期结构。依据实验结果,分析了脉冲数对周期性条纹结构周期变化的影响。研究结果为硅材料表面微结构加工提供了参考。
激光光学 飞秒激光 微结构 偏振 光学学报
2014, 34(s1): s114002





